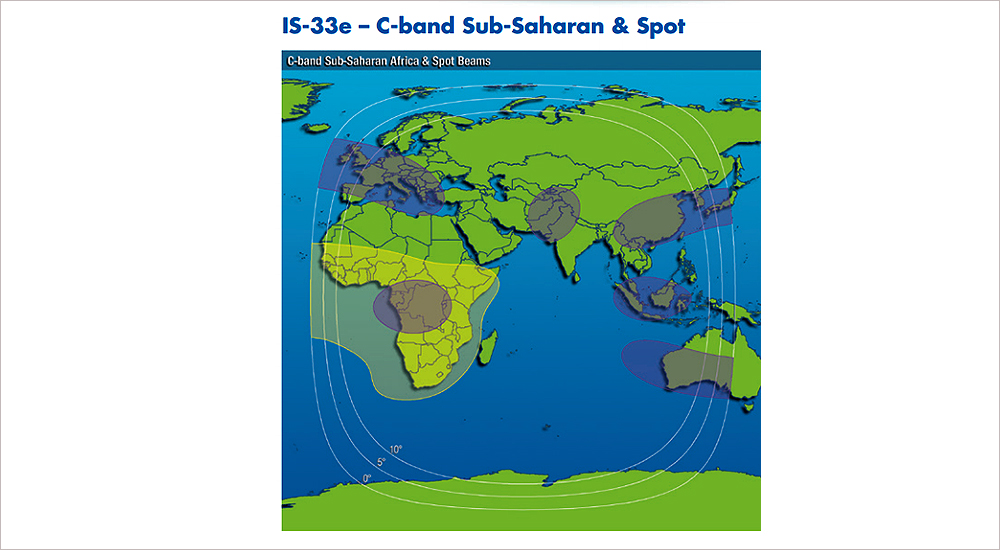
Intelsat, operator of the world’s first globalised network, powered by its satellite backbone, announced that Sonema has extended its agreement for satellite services to support enterprise networks in Africa. Sonema, a telecommunications service provider based in Monaco, supports more than 650 VSAT sites for banking and financial institutions across Africa. The majority of the networks are supported by C-band services from Intelsat 14, located at 315° East, and Intelsat 904, located at 60° East.
Under the multi-year extension, Sonema will integrate C-band connectivity from the Intelsat 33e satellite to expand services to more remote regions of Africa. The combination of Intelsat 14 and Intelsat 33e allows Sonema to provide customised solutions, with a focus on robustness and high quality of experience, to its customers
“The banking sector is a major growth engine for Africa. As such, our customers depend on the highly reliable and secured corporate networks we deploy and maintain for them,” said Catherine Delom, Managing Director of Sonema.
“Intelsat has provided us high-quality, dependable satellite connectivity for years. The Intelsat EpicNG platform will also enable the option to offer our customers new, innovative solutions and services that can be easily delivered via C-band and Ku-band spot beams to the most remote locations.”
“From our long history of serving customers in Africa, we know that enterprise customers need access to highly reliable and more effective bandwidth to meet growing demands,” said Jean-Philippe Gillet, Intelsat’s Vice President, Europe, Middle East and Africa Sales.
“We are providing the bandwidth essential to improving the end customer experience. This agreement ensures that Sonema’s customers will be able to expand their operations knowing that each of their sites will have access to the same level of reliable broadband connectivity, regardless of location.”
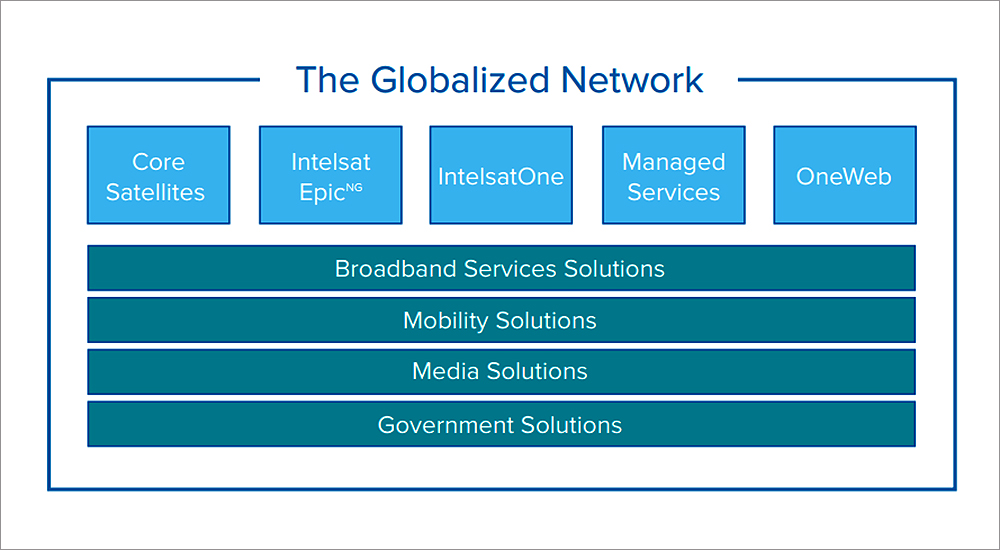
Intelsat operates the world’s first globalised network, delivering high-quality, cost-effective video and broadband services anywhere in the world. Intelsat’s globalised network combines the world’s largest satellite backbone with terrestrial infrastructure, managed services and an open, interoperable architecture to enable customers to drive revenue and reach through a new generation of network services.
Thousands of organisations serving billions of people worldwide rely on Intelsat to provide broadband connectivity, multi-format video broadcasting, secure satellite communications and seamless mobility services.
What is Intelsat EpicNG broadcast technology
Intelsat designed its next-generation platform, Intelsat EpicNG, to meet the demands of the new global broadband infrastructure. Intelsat EpicNG is designed to provide higher throughput and efficiency in an open architecture platform, providing highly reliable next-generation capabilities that build upon operators’ existing networks.
The Intelsat EpicNG platform represents the progressive evolution of Intelsat’s leading global satellite and terrestrial infrastructure. Intelsat EpicNG incorporates C, Ku and Ka spot beams in a high-performance platform that delivers significantly more capacity and more throughput per unit of spectrum, an important technical and economic benefit for service providers delivering solutions customised for specific regions or applications.
Intelsat EpicNG will serve telecommunications and value-added service providers that need to satisfy these connectivity demands, as well as energy, maritime, aeronautical, media, corporate networking and government customers that require broadband applications for the distribution and collection of content to regions often out of reach of traditional terrestrial connections.
More than 90% of the commercial satellite industry customer base is comprised of professional, carrier or enterprise-grade service providers offering service in the C and Ku bands. Intelsat EpicNG is designed to build upon the success of these commercial and governmental entities, allowing them to expand offerings and enter new regions and vertical markets without abandoning previous infrastructure investments.
Spectrum is a valuable resource. Irrespective of the frequency band C, Ku, Ka, there is a limited amount of spectrum available, so it needs to be utilised efficiently. One approach is to employ frequency reuse, which refers to a satellite using the same frequency multiple times simultaneously. The more frequency reuse supported, the greater the total bandwidth that spectrum can deliver. Frequency reuse is a concept that is used both terrestrially and on satellites.
Intelsat has implemented frequency reuse in its satellites for several decades. It has been employed by traditional wide-beam satellites but in a relatively limited way. While using the same frequencies beams cover different regions of the Earth. Similarly, beams use the same frequency, with different coverage. Different types of polarisation, or orientation, of transmissions are used to further differentiate signals to avoid interference.
Intelsat EpicNG takes advantage of satellite antenna technology that enables multiple smaller beams to be deployed. This is similar to how consumer-focused Ka-band platforms have been deployed over small regions, but in this case, the implementation is expanded to the frequency band and beam configuration that
Each beam represents a unique combination of frequency and polarisation. Any beam of a given frequency and polarisation is separated by one beam width from other beams. This separation is necessary to avoid interference between beams of the same frequency and polarisation. Other frequency reuse schemes are possible, based on the amount of spectrum available and the amount of spectrum serving a given area. Many have the false impression that spot beam frequency reuse is restricted to Ka-band. Intelsat EpicNG will apply multi-spot technology to Ku-band and C-band, as well as Ka-band.
The physics of satellite communications are well understood: for the same satellite power, the same spot beam size and the same terminal size, all frequency bands provide the same throughput in clear sky conditions. The selection of the best frequency for a given application is therefore driven by many other considerations.
There are several high throughput satellites either in operation or nearing deployment. While they each have distinct features, a common design element among most of these systems, typically Ka-band, is a network topology that limits connectivity and has lower isolation of co-channel spots. As a result, most of these systems are designed with an architecture that is proprietary and closed. This topology is a severe limitation for many operators.
Intelsat EpicNG allows connectivity among multiple spot beams, including star and mesh, as well as loopback within the same user beam.
This guarantees backward compatibility with existing networks, and forward compatibility with full flexibility to evolve the network design and technology as and when customers want.
The use of multi-spot C-band and Ku-band in a bent-pipe architecture will allow for an open network architecture that is backward-compatible in most instances with operator current network infrastructure, and is future-proof depending on existing network configuration. This will enable service providers to easily implement Intelsat EpicNG into their existing architecture, building upon their current business success and limiting the hardware investment they will need to make. Operators will use the hardware of their choice and customise their service characteristics.
The mix of spectrum available C, Ku and Ka bands, through Intelsat EpicNG will let network operators and value-added service providers improve the quality of their service in a cost- efficient manner while maintaining control of their own systems.
The Intelsat EpicNG satellites will provide four to five times more bandwidth capacity in MHz than traditional satellites. This is as a result of frequency reuse through spot beams. In addition, because of the higher power available per spot beam and a prudent design that minimises RF interference between spots, the efficiency number of bits per MHz will be multiplied by two to three times. In total, the expected aggregate throughput on an Intelsat EpicNG satellite will vary according to application served and satellite but is anticipated to be in the range of 25-60 Gbps.
Whereas most high throughput satellites offer a best effort, contended service using proprietary ground equipment, Intelsat EpicNG offers Committed Information Rate MHz using operator-selected ground platforms. The use of spot beams on Intelsat EpicNG provides additional benefits that translate into improved spectral efficiency offered to customers – the Mbps that can be achieved in a MHz of satellite bandwidth.
Some customers will benefit from consolidation of their capacity from multiple satellites onto one or two Intelsat EpicNG satellites. Others will benefit from the high throughput in a given region or from the high efficiency that enables the use of small terminals. The specific benefits will depend on the application and the customer requirements.