5G features have matched or exceeded expectations for a majority of early adopters and organizations are optimistic about the opportunities that it offers, according to the Capgemini Research Institute.
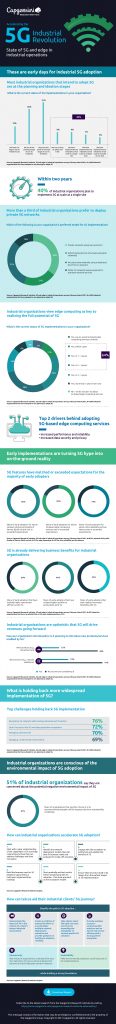
According to Accelerating the 5G Industrial Revolution: State of 5G and edge in industrial operations report released by the Capgemini Research Institute, industrial 5G adoption is still at the ideation and planning stages, with only 30% of industrial organizations having moved to the pilot stage or beyond. This means there is a huge window of opportunity for telcos and those industrial organizations that are yet to make a move.
Signaling a paradigm shift, 40% of industrial organizations surveyed expect to roll out 5G at scale at a single site within two years and the experience of early adopters could persuade others to make the move. 5G trials and early implementations are delivering strong business benefits, with 60% of early adopters saying that 5G has helped to realize higher operational efficiency, while 43% say they have experienced increased flexibility.
The study also found that industrial organizations are optimistic that 5G will drive revenues by enabling the introduction of new products, services and business models. In fact, 51% of industrial organizations plan to leverage 5G to offer new products and 60% plan to offer new services enabled by 5G.
Furthermore, industrial organizations are aware of the role of Edge Computing in their 5G initiatives and view it as essential to realizing the full potential of 5G. A total of 64% of organizations plan to adopt 5G-based Edge Computing services within three years, driven by the increased performance, reliability, data security and privacy it offers. More than a third of industrial organizations across sectors surveyed prefer to deploy private 5G networks, with interest in private 5G networks led by the semiconductor and high-tech sector (50%), followed by aerospace and defense (46%).
Challenges remain for widespread adoption
The report highlights that, to make the most of 5G’s potential, organizations will need to address a number of challenges, including:
- Integrating 5G with existing networks and IT systems: organizations are finding that the lack of standardized, interoperable solutions result in increased time for assembly and testing;
- Defining 5G use cases and estimating their return on investment, especially in brownfield environments, where a return needs to be measured against existing options like wired connections and the cost of replacing cables;
- Managing cybersecurity due to difficulties in selecting trusted or qualified vendors, anticipating the security impact of different network deployment scenarios and a lack of internal processes to reduce exposure to risk. As many as 70% of industrial organizations surveyed view the management of cybersecurity as a key challenge associated with 5G implementations;
Orchestrating a multi-vendor environment to deliver the multiple functional components that industrial 5G solutions consist of is another challenge. As many as 69% of industrial organizations view identifying, onboarding and managing multiple vendors as a key barrier.
G for green?
5G offers many direct and indirect environmental benefits through its inherently energy-efficient design and its ability to enable environmental and sustainability-focused use cases. But industrial organizations are also aware of areas of environmental concerns and are already considering ways to tackle this.
More than half (53%) of industrial organizations surveyed say that reducing the environmental impact of their 5G implementations is a priority, while 67% plan to take the sustainability credentials of 5G operators, vendors and suppliers into account as part of their 5G procurement decisions.